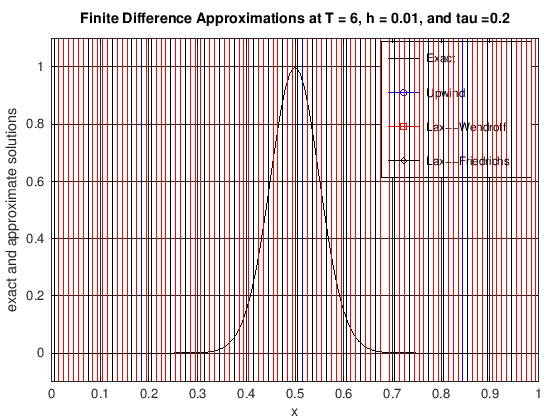
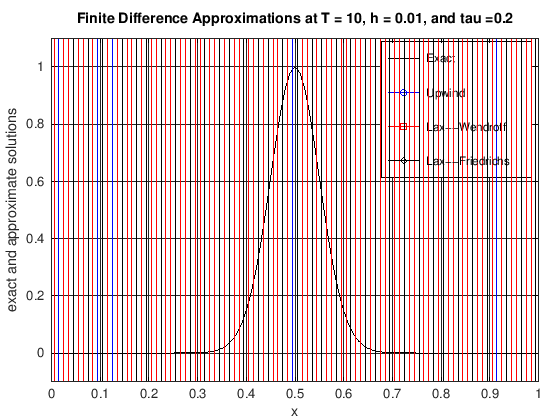
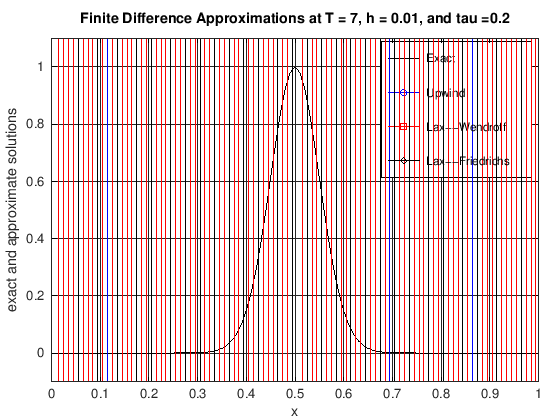
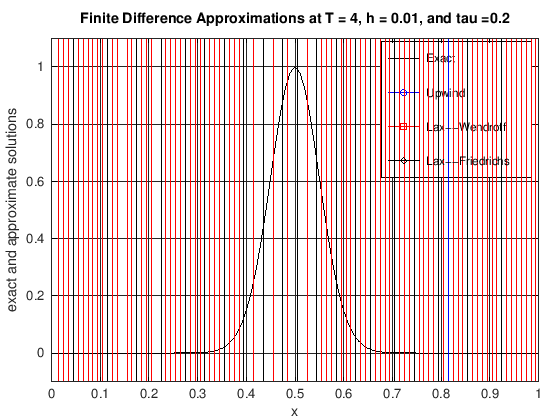
function [errorUW, errorLW, errorLF] = AdvectionPer(finalT, ...
N, K, numPlots, typeInit)
% This function computes numerical approximations to solutions
% of the linear advection equation
%
% u_t + u_x = 0
%
% using the upwind (UW), Lax-Wendroff (LW), and Lax-Friedrichs
% (LF) methods on the periodic domain [0,1]. The initial data is
% constructed from either a square or a triangular wave.
%
% Input
% finalT : the final time
% N : the number of spatial grid points in [0,1]
% K : the number of time steps in the interval [0,finalT]
% numPlots : the number of output frames in the time interval
% [0,finalT]. Must be a divisor of K.
% typeInit : is the type of initial condition
% = 1 for the Gaussian wave
% = 2 for the triangular wave
% = 3 for the square wave.
%
% Output
% errorUW: the max norm error of the UW scheme at t = finalT
% errorLW: the max norm error of the LW scheme at t = finalT
% errorLF: the max norm error of the LF scheme at t = finalT
%
errorUW = 1.0;
errorLW = 1.0;
errorLF = 1.0;
if N > 0 && N - floor(N) == 0
h = 1.0 / N;
else
display('Error: N must be a positive integer.')
return
end
if (K > 0 && K - floor(K) == 0) && finalT > 0
tau = finalT / K;
else
display('Error: K must be a positive integer, and')
display(' finalT must be positive.')
return
end
mu = tau / h;
x = 0:h:1.0;
uo = zeros(1, N + 1);
if typeInit == 1
uo = exp(-20 * (sin(pi * (x - 0.5))).^2);
elseif typeInit == 2
uo = triangle(N, 0);
elseif typeInit == 3
uo = square(N, 0);
else
display('No such initial condition.')
return
end
uoUW = zeros(1, N + 1); uUW = zeros(1, N + 1);
uoLW = zeros(1, N + 2); uLW = zeros(1, N + 2);
uoLF = zeros(1, N + 2); uLF = zeros(1, N + 2);
uExact = zeros(1, N + 1);
uoUW = uo;
uoLW = uo; uoLW(N + 2) = uo(2);
uoLF = uo; uoLF(N + 2) = uo(2);
if mod(K, numPlots) == 0
stepsPerPlot = K / numPlots;
else
display('Error: numPlots is not a divisor of K.')
return
end
for k = 1:numPlots
for j = 1:stepsPerPlot
kk = (k - 1) * stepsPerPlot + j;
for ell = 2:N + 1
uUW(ell) = (1 - mu) * uoUW(ell) + mu * uoUW(ell - 1);
uLW(ell) = uoLW(ell) - 0.5 * mu * (uoLW(ell + 1) ...
-uoLW(ell - 1)) + 0.5 * mu * mu * (uoLW(ell + 1) ...
-2.0 * uoLW(ell) + uoLW(ell - 1));
uLF(ell) = 0.5 * (uoLF(ell + 1) + uoLF(ell - 1)) ...
-0.5 * mu * (uoLF(ell + 1) - uoLF(ell - 1));
end
uUW(1) = uUW(N + 1);
uoUW = uUW;
uLW(1) = uLW(N + 1); uLW(N + 2) = uLW(2);
uoLW = uLW;
uLF(1) = uLF(N + 1); uLF(N + 2) = uLF(2);
uoLF = uLF;
end
currTime = tau * kk;
if typeInit == 1
uExact = exp(-20 * (sin(pi * (x - 0.5 - currTime))).^2);
elseif typeInit == 2
uExact = triangle(N, currTime);
elseif typeInit == 3
uExact = square(N, currTime);
end
hf = figure(k);
clf
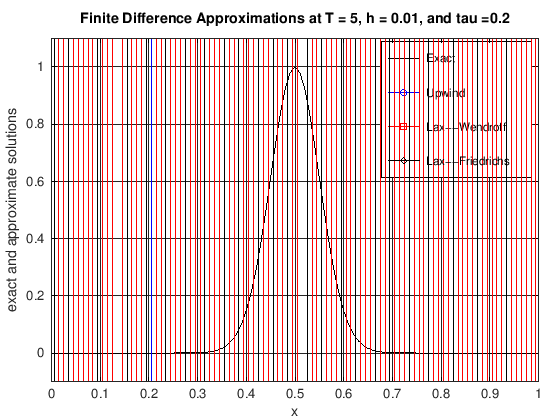
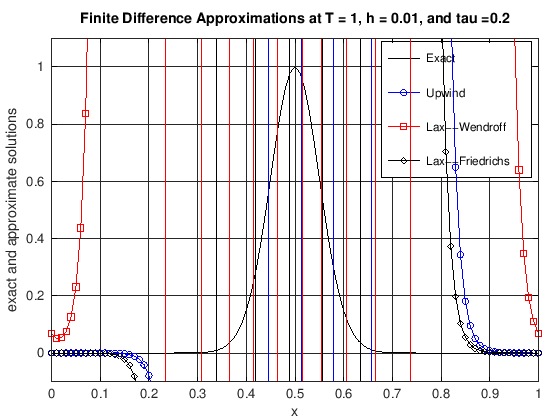
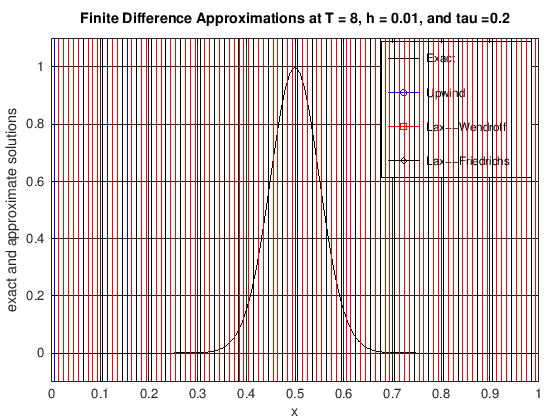
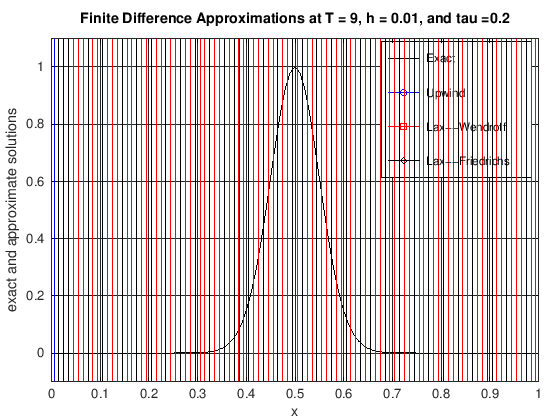
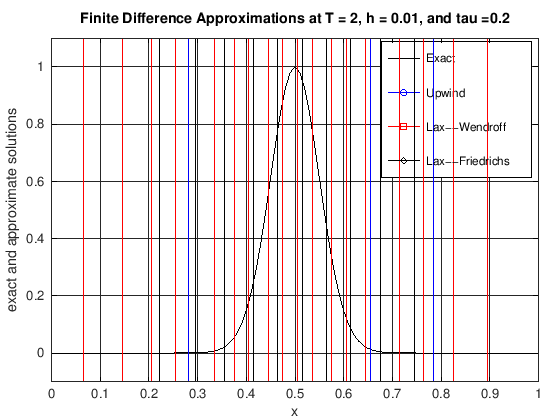
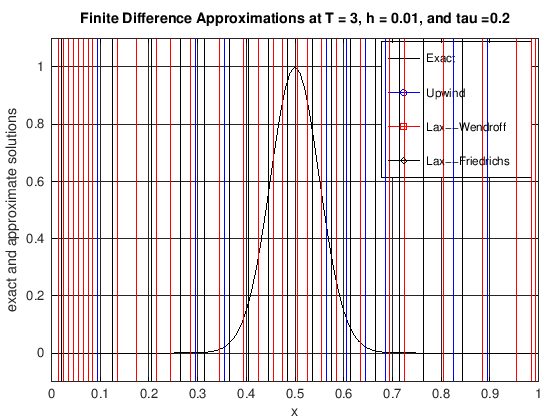
plot(x, uExact, 'k-', x, uUW, 'b-o', x, uLW(1:N + 1), 'r-s', x, ...
uLF(1:N + 1), 'k-d')
grid on;
xlabel('x');
ylabel('exact and approximate solutions');
title(['Finite Difference Approximations at T = ', ...
num2str(currTime), ', h = ', num2str(h), ...
', and tau =', num2str(tau)]);
legend('Exact', 'Upwind', 'Lax--Wendroff', 'Lax--Friedrichs')
axis([0, 1, -0.1, 1.1])
set(gca, 'xTick', 0:0.1:1)
s1 = ['000' num2str(k)];
s2 = s1((length(s1) - 3):length(s1));
s3 = ['OUT/adv', s2, '.pdf'];
%exportgraphics(gca, s3)
end
errorUW = max(abs(uExact - uUW));
errorLW = max(abs(uExact - uLW(1:N + 1)));
errorLF = max(abs(uExact - uLF(1:N + 1)));
end